Implementing caching in an API function Last updated: 27. Nov 2025
This function implements caching for an API endpoint by checking the 'If-Modified-Since' header and returning a 304 status if the content has not been modified.
Implementation steps:
Server-Side (API): setHeader "Last-Modified" and check If-Modified-Since
Client-Side: Make sure caching is enabled (if so, nothing needs to be changed)
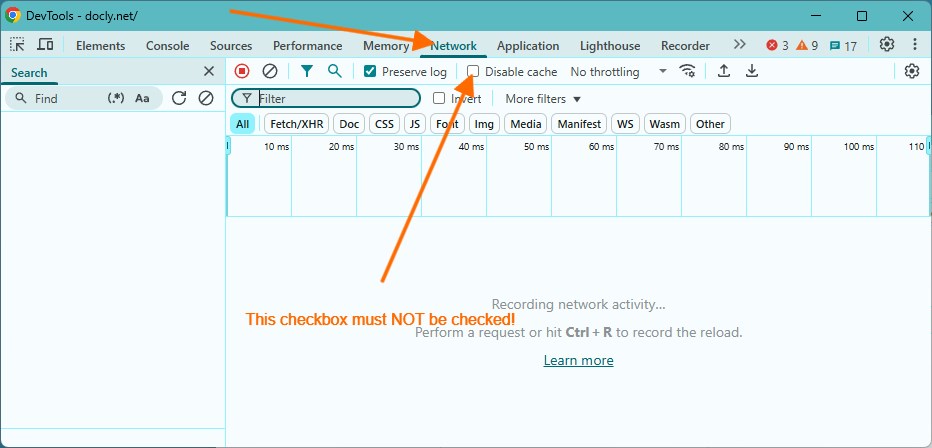
Testing: Make sure you haven't disabled caching in the developer toolbar
- Server-Side: setHeader "Last-Modified" and check If-Modified-Since
// Format the site's last modified date
const formattedSiteModifiedDate = docly.format(request.sitemodified, "R");
docly.setHeader("Last-Modified", formattedSiteModifiedDate);
// Retrieve the 'If-Modified-Since' header from the request
const ifModifiedSinceHeader = docly.getHeader("If-Modified-Since");
if (ifModifiedSinceHeader) {
const ifModifiedSinceDate = new Date(ifModifiedSinceHeader);
const dateDifference = docly.dateDiff(ifModifiedSinceDate, request.sitemodified);
// If the difference in seconds is less than 1, return 304 (Not Modified)
if (dateDifference.TotalSeconds < 1) {
return docly.setResultCode(304);
}
}
// Return the response object (not cached)
return {
ifModified: ifModifiedSinceHeader,
siteModified: formattedSiteModifiedDate,
diff: dateDifference?.TotalSeconds
}; - Client-Side: Make sure caching is enabled (if so, nothing needs to be changed)
Modern browsers generally cache responses based on HTTP headers (like Last-Modified or ETag). While the standard fetch API respects these headers, jQuery's AJAX functions (like $.get or $.ajax) might append a cache-busting parameter (_={timestamp}) by default for certain data types.
To ensure caching is allowed for a $.get request, explicitly set the cache option to true:
// Example: Using $.get with caching explicitly enabled
$.get("API/test").then(function(data) {
// Handle the response data here
console.log("Data received:", data);
}).fail(function(jqXHR, textStatus, errorThrown) {
// Handle errors
console.error("Request Failed:", textStatus, errorThrown);
});